Ultimate abstract base class for all C++ measurement algorithms. More...
#include <Algorithm.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual void | fail (afw::table::SourceRecord &measRecord, MeasurementError *error=nullptr) const =0 |
| Handle an exception thrown by the current algorithm by setting flags in the given record. | |
| virtual | ~BaseAlgorithm ()=default |
| std::string | getLogName () const |
Protected Attributes | |
| std::string | _logName |
Detailed Description
Ultimate abstract base class for all C++ measurement algorithms.
New algorithms should not inherit directly from this class.
Definition at line 44 of file Algorithm.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ ~BaseAlgorithm()
|
virtualdefault |
Member Function Documentation
◆ fail()
|
pure virtual |
Handle an exception thrown by the current algorithm by setting flags in the given record.
fail() is called by the measurement framework when an exception is allowed to propagate out of one the algorithm's measure() methods. It should generally set both a general failure flag for the algorithm as well as a specific flag indicating the error condition, if possible. To aid in this, if the exception was an instance of MeasurementError, it will be passed in, carrying information about what flag to set.
An algorithm can also to chose to set flags within its own measure() methods, and then just return, rather than throw an exception. However, fail() should be implemented even when all known failure modes do not throw exceptions, to ensure that unexpected exceptions thrown in lower-level code are properly handled.
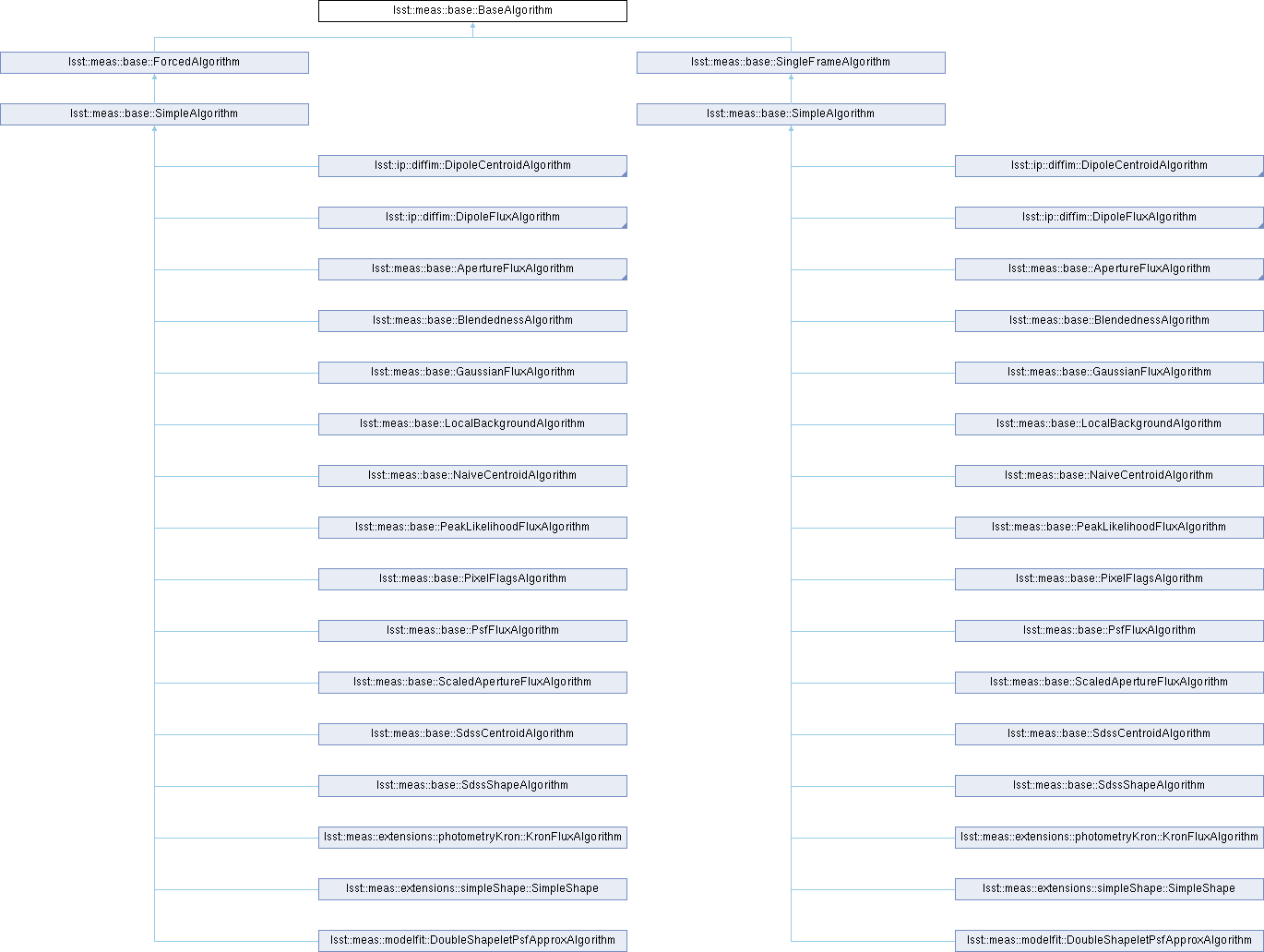
Implemented in lsst::ip::diffim::PsfDipoleFlux, lsst::meas::base::ApertureFluxAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::BlendednessAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::GaussianFluxAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::LocalBackgroundAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::PeakLikelihoodFluxAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::PixelFlagsAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::PsfFluxAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::ScaledApertureFluxAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::SdssCentroidAlgorithm, lsst::meas::base::SdssShapeAlgorithm, lsst::meas::extensions::photometryKron::KronFluxAlgorithm, lsst::meas::extensions::simpleShape::SimpleShape, and lsst::meas::modelfit::DoubleShapeletPsfApproxAlgorithm.
◆ getLogName()
|
inline |
Definition at line 66 of file Algorithm.h.
Member Data Documentation
◆ _logName
|
protected |
Definition at line 69 of file Algorithm.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- /j/snowflake/release/lsstsw/stack/lsst-scipipe-12.1.0/Linux/meas_base/g3e17d7035e+5b3adc59f5/include/lsst/meas/base/Algorithm.h
Generated on Thu Nov 27 2025 09:15:18 for LSST Applications by